
英语原文共 6 页,剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
Effects of pilot fuel quantity on the emissions characteristics of a CNG/ diesel dual fuel engine with optimized pilot injection timing
Jie Liu a, Fuyuan Yang a, , Hewu Wang a, Minggao Ouyang a, Shougang Hao b
a State Key Laboratory of Automotive Safety and Energy, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, PR China b Changzhou ECTEK Automotive Electronics Limited, Changzhou City, 213164, PR China
引燃油量对优化天然气/柴油双燃料发动机的微喷正时排放特性的影响
刘杰,杨福源,王贺武,欧阳明高,郝守刚
汽车安全与能源国家重点实验室,清华大学,北京 10084,中国常州常州易控汽车电子有限公司,常州市,213164,中国
Highlights
亮点
Emission characteristics of the CNG/diesel dual fuel engine. NOx emissions averagely reduced by 30%.The unburned HC emissions are obviously higher.Around 90% of the THC emissions were unburned methane. PM was increased with the increase of pilot diesel quantity.
天然气/柴油双燃料发动机的排放特性。氮氧化合物(NOx)排放量平均减少30%。未燃烧的碳氢化合物(CH)排放量明显更高。总烃类(THC)中大约有90%是未燃烧的甲烷。颗粒物(PM)的排放量随着引燃柴油量的增加而增加。
Article info
Article history:
Received 7 October 2012
Received in revised form 8 March 2013 Accepted 10 March 2013
Available online 11 May 2013
文章信息
文章历史:
2012年十月7号修订
2013年三月8号到10号修订表格
2013年五月11号上传到网络
Keywords:Dual fuel CNG Emission CI engine
关键词:双燃料 天然气 排放 压燃式发动机
Abstract
For CNG/diesel dual fuel engines, the effects of pilot fuel quantity and injection timing are noticeable and significant. In this study,the emission characteristics of a CNG–diesel dual fuel engine with different pilot diesel fuel quantity and optimized pilot injection timing were investigated. The CO emission levels under dual fuel mode are considerably higher than that under normal diesel operation modes even at high load, which indicated that there exist some flame extinction regions.Dual fuel mode reduces NOx emissions by 30% averagely in comparison to diesel mode. That is because most of the fuel is burned under lean pre-mixed conditions which result in lower local temperature. The unburned HC emissions under dual-fuel mode are obviously higher than that of the normal diesel mode, especially at low to medium loads. And around 90% of the THC emissions were unburned methane, which means the flame does not prop-agate throughout the charge. THC emissions reduce significantly with the increase of the pilot diesel quantity. Thanks to the premixed nature of the combustion mode and the methane molecular structure, the PM emission is reduced obviously under dual fueling condition. The PM emission is increased with the increase of the pilot fuel quantity.
2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
摘要
对天然气/柴油双燃料发动机,引燃油量和喷油定时的影响十分显著。在这项研究中,对双燃料发动机在不同引燃油量和微喷正时的排放特性进行了研究。双燃料模式下的一氧化碳的排放水平高于正常柴油机运行模式,即使在高负荷下,表明存在一些没有火焰的区域。双燃料模式下氮氧化合物相比正常柴油机模式减少了30%。这是因为大部分的燃料在预混合条件下燃烧而导致局部温度降低。双燃料模式下的未燃烧的碳氢化合物排放量冥想高于正常柴油机模式,尤其是在低中等负荷。总烃类中大约百分之90是未燃烧的甲烷,这意味着火焰不支持在预混合整个过程。总烃类的排放随着引燃柴油量增加而增加。由于燃烧模式的预混合性质和甲烷的分子结构,在双燃料条件下,颗粒物排放明显减小。颗粒物排放量随引燃油量的增加而增加。
2013 Elsevie公司版权所有
1.Introduction
With rising fuel price and more stringent emission legislation, recent researches are focus on high efficiency and low emissions technologies in the field of internal combustion engines [1]. In or-der to simultaneously reduce soot and NOx emissions while achieving high thermal efficiency, many strategies have been pro-posed in compression ignition (CI) engine. The low temperature premixed combustion is employed by most of the strategies, and the ultimate goal is to achieve Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) combustion with near zero NOx and soot emissions [2,3]. However, the controllability of the heat release rate and the ignition timing is the challenge of the HCCI concept.
- 引言
随着燃油价格的上涨和排放法规的日益严格,近年来国内外的研究主要集中在内燃机领域的高效低排放技术[1]。为了同时降低烟尘和NOx排放,同时实现高热效率,许多策略已经提出了压缩点火(压燃式)发动机。低温预混合燃烧技术被大多数策略所采用,最终目标是实现均质压燃和近零氮氧化合物和烟尘的排放[2,3]。然而,放热率和点火正时的可控性是均质压燃概念的挑战。
In order to address these problems, dual fuel combustion con-cept was utilized by many researchers. With port injection of a low-reactivity fuel combining direct in-cylinder injection of a high-reactivity fuel, the combustion phasing and duration can be flexibly controlled through reactivity gradient [4–7]. A higher oc-tane number (ON) indicates a higher resistance to auto-ignition, which in turn can effectively extend the upper load limit of the dual fuel engine without using too much EGR. From this point of view, natural gas with large proven reservesand high ON is the best choice of the port injection fuel.
为了解决这些问题,双燃料燃烧的概念被许多研究人员所利用。在高反应性燃料的缸内喷射中加入低反应性燃料的端口喷射,通过反应性梯度来灵活控制燃烧相位和持续时间 [4–7]。较高的辛烷值表示较高自动点火电阻,这反过来又可以有效延长双燃料发动机上的负载的限制而没有使用过多的废气再循环。从这个角度来看,天然气探明储量大和辛烷值高是喷射燃料的最佳选择。
The study of Papagiannakis et al. shows that the maximum explosion pressure of the diesel ignited natural gas engine is lower than that of the original diesel engine. And at high loads, the com-bustion duration is shorter than that of the original diesel engine [8]. NOx and soot emissions are lower compared with the original diesel engine [9–11]. At Low loads, however, the diesel ignited nat-ural gas engine has higher CO and unburned HC emissions [12,13].
Papagiannakis等人的研究,表明使用天然气的柴油发动机最大爆炸压力低于原来的柴油机。并在高负荷下,燃烧的持续性比原来的柴油机更短[8]。氮氧化合物和烟尘排放量也低于原柴油机[9–11]。在低负荷下,然而,燃烧天然气柴油发动机的一氧化碳和未燃烧碳氢化合物更高。
Through the intake air throttle valve and EGR valve controlling the air–fuel ratio of the diesel-ignited natural gas engine, the emission characteristics of the diesel ignited natural gas engine at low load can be improved significantly [14,15]. By changing the EGR rate and fuel injection timing to generate a two-stage ignition, a higher thermal efficiency and lower NOx emissions can be obtained [16].
通过进气节流阀和废气再循环阀来控制柴油引燃的天然气发动机的空气燃料比,柴油引燃的天然气发动机的发射特性在低负荷时可以显著改善[14,15]。通过改变废气再循环效率和喷油定时来生成一个二级点火,可以获得更高的热效率和更低的氮氧化合物排放[16]。
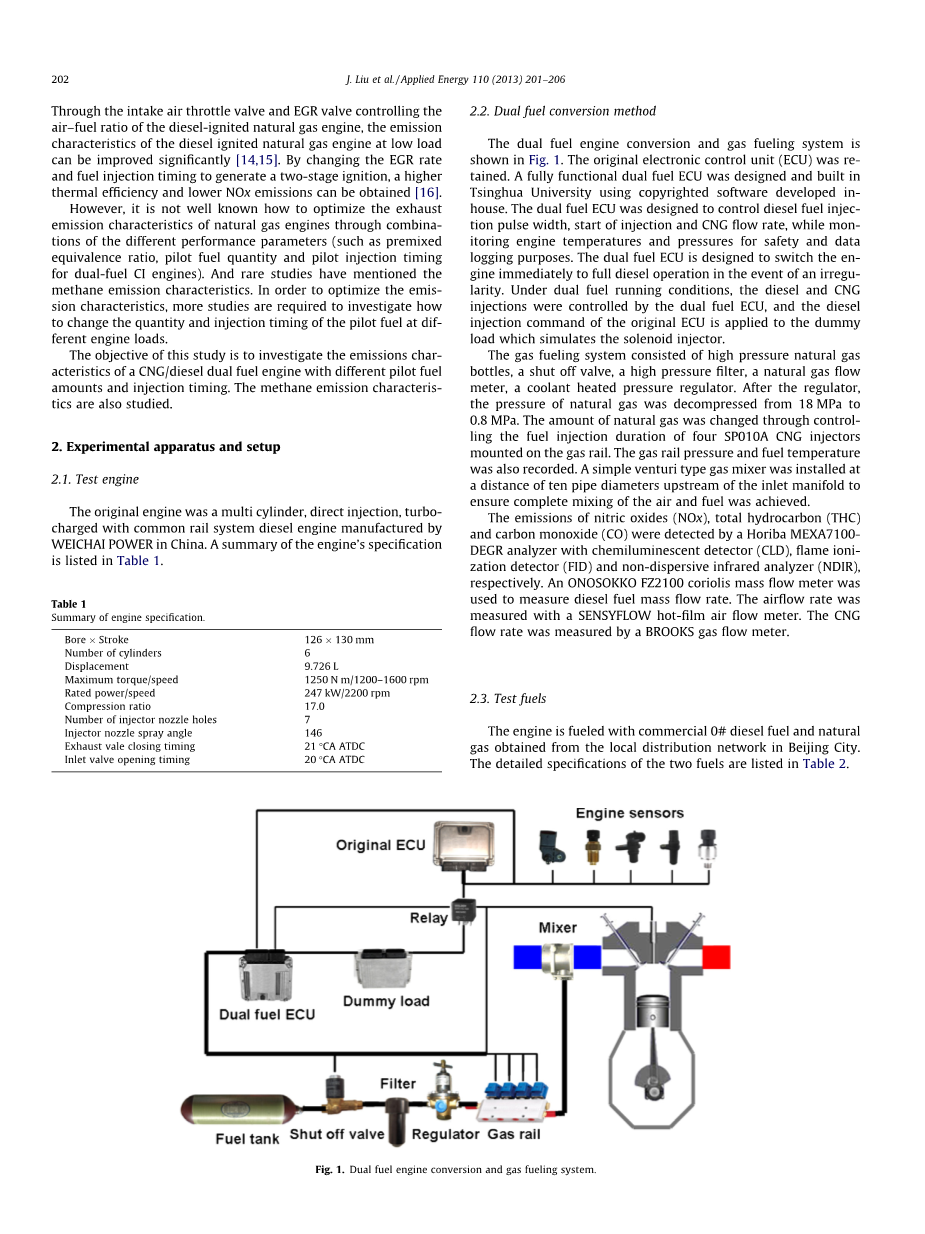
However,it is not well known how to optimize the
剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
资料编号:[138153],资料为PDF文档或Word文档,PDF文档可免费转换为Word


